Exhaled breath contains many small molecules that might be related to the condition of human and animal bodies. Measuring these biomarkers has the potential of replacing commonly used medical (blood) tests. In a project of SenzAir, a Dutch company developing devices for breath analysis, a demonstrator was developed in co-creation with LioniX, Lode, MESA+/University of Twente and Relitech. This system can measure online the concentration of ammonia in exhaled breath, and also in other gas or fluid mixtures.
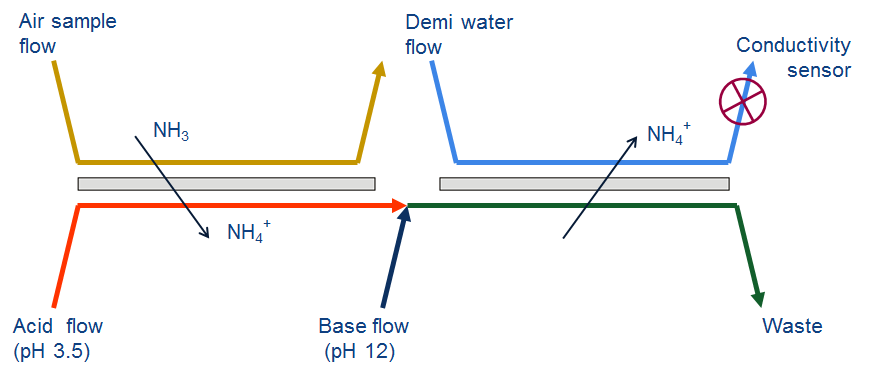
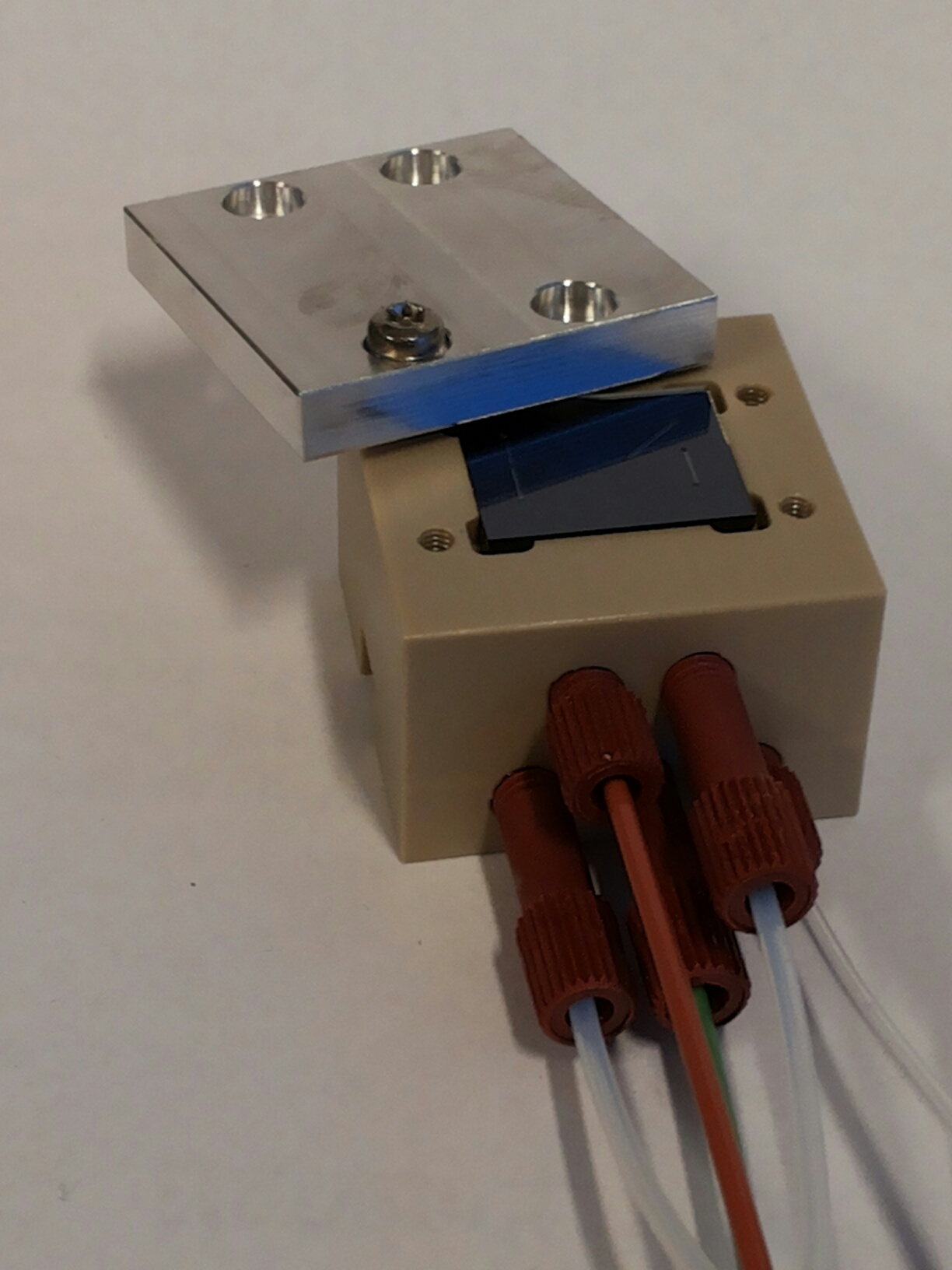
A micro-fluidic sensor chip was developed to measure concentrations of NH3 in the ppb-ppm-range by the University of Twente and Lionix. This chip was incorporated in a demonstrator that enables sampling of exhaled breath and delivering the NH3-containing air sample to the chip. The main challenge for Relitech in this project was to bring the specialized, sensitive sensor from the lab to the hospital. We successfully integrated the microfluidic chip in a casing and prevented loss of NH3 on its way from the patient to the sensor. Also, we developed the software to run the demonstrator and validated and calibrated the product using well defined gas-mixtures. Finally, we assisted in the setup, execution and interpretation of the first clinical trials in Radboud UMC.
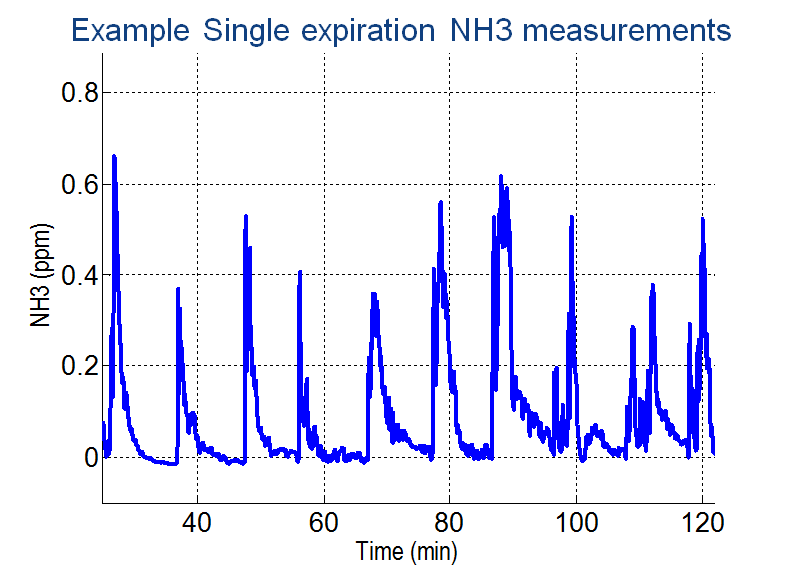
See also the presentation on this project on Sense of Contact.